Table of Contents
Get Custom eCommerce Fulfillment Service
Book a Meeting
What Are the Differences Between Shipping and Freight
Time: Sep 29,2024 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
When it comes to moving goods from point A to point B, we often hear terms like "shipping" and "freight" being thrown around. But do they mean the same thing? Not exactly. While both involve transporting products, the specifics of shipping and freight differ in key ways that can affect costs, logistics, and delivery methods.
1. What Is Shipping
Shipping refers to the process of transporting smaller goods, typically via standard parcel carriers like UPS, FedEx, or USPS. It’s most commonly associated with e-commerce and retail businesses that ship individual items or small packages directly to consumers.Key characteristics of shipping include:
Parcel Size: Shipping typically involves smaller items, usually less than 150 lbs.Method: Shipping often involves transportation via ground, air, or sea but is mostly tied to ground shipping in daily use.
Carriers: Common shipping carriers include UPS, FedEx, DHL, and postal services.
Cost: Shipping costs are usually calculated based on weight, dimensions, and delivery speed.
Tracking: Most standard shipping services offer real-time tracking for parcels.
2. What Is Freight

Key characteristics of freight include:
Shipment Size: Freight covers larger shipments, typically over 150 lbs. It can include anything from large industrial machinery to dozens of pallets of products.Method: Freight can be transported via trucks, ships, trains, or planes. There are two main types: Full Truckload (FTL) and Less-than-Truckload (LTL).
Carriers: Freight carriers include specialized companies like XPO Logistics, JB Hunt, and YRC Freight.
Cost: Freight pricing is usually determined by weight, distance, freight class, and type of shipping method used.
Tracking: Freight often provides detailed tracking but typically isn’t as detailed as parcel services.
3. Shipping vs. Freight: a Detailed Comparision
Shipping |
Freight | |
| Shipping Sizes | Small Packages (typically under 150 lbs) |
Large, bulk shipments (over 150 lbs) |
| Common Uses | E-commerce, retailer, small parcel deliveries |
B2B, large or industrial shipments |
| Transpotation Methods | Ground, Air, Sea (Parcel carriers) |
Trucks, ships, air, rail (LTL, FTL, containers) |
| Cost Calculation | Weight, demensions, delivery speed |
Weight, distance, freight class, bulk rates |
| Delivery Speed | Fast (1-7 days depending on services) |
Slower for large shipments (can take weeks) |
| Carriers | FedEx, USPS, UPS, DHL |
XPO Logistics, JB Hunt, YRC Freight and Others |
| Tracking | Real-time, detailed tracking |
Less frequent tracking, especially for sea or international |
| Handling | Handled with care for smaller packages |
Forklifts, pallets, large machinery handling |
| Ideal for | Consumers, small businesses |
Large business, manufacturers, wholesales |
| Insurance | Available for small packages |
Offered for large cargo, often necessary for valuable items |
| Door-to-door delivery | Yes (for small packages) |
Sometimes; depends on freight services chosen |
| Cost-efficiency | Cheaper for small items |
More cost-effective for large or bulk items |
| Customization Options | Standardized services (express, priority) |
Highly customizable (FTL, LTL, specific needs) |
4. Differences Between Shipping and Freight
While shipping and freight both involve moving goods from one point to another, the differences between them stem from several key factors:Size and Weight Limitations
As we’ve previously outlined, shipping services generally cater to packages under 150 pounds, while freight services handle much larger shipments. If your shipment exceeds the size and weight limitations of standard parcel delivery services, you’ll need to opt for a freight solution.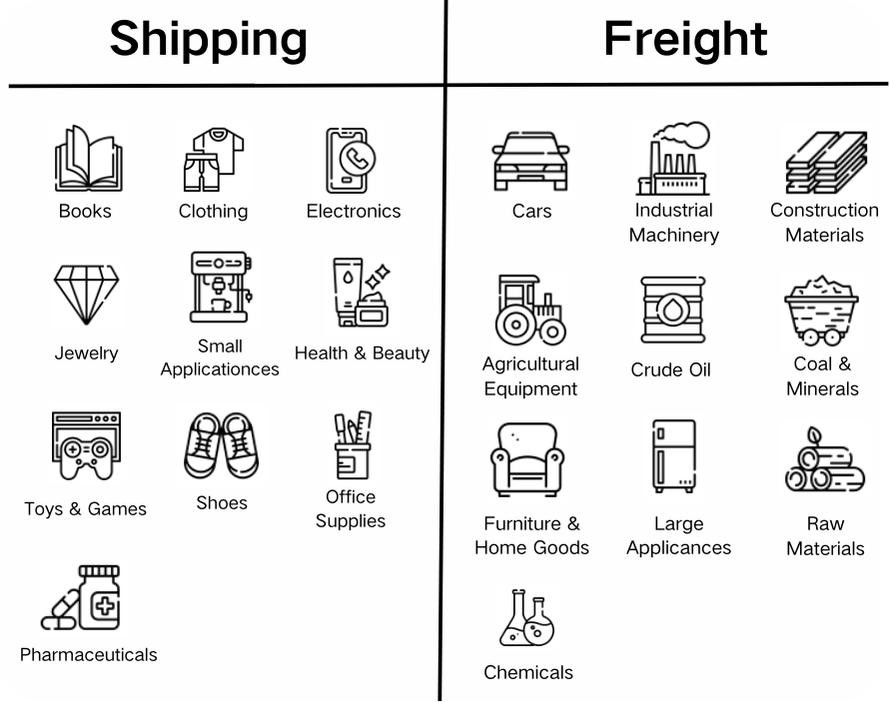
Cost Efficiency
Freight is generally more cost-effective for larger shipments due to economies of scale. The larger the shipment, the lower the cost per unit, making it the preferred choice for businesses moving large quantities of goods. Shipping, on the other hand, is convenient for small to medium packages but can be expensive when calculated per unit of weight.Cost Efficiency
Freight is generally more cost-effective for larger shipments due to economies of scale. The larger the shipment, the lower the cost per unit, making it the preferred choice for businesses moving large quantities of goods. Shipping, on the other hand, is convenient for small to medium packages but can be expensive when calculated per unit of weight.Handling and Logistics
Shipping is often straightforward, involving pre-packaged goods with less complex logistics. Freight, however, requires more coordination, often involving specialized loading, handling equipment, and paperwork. Freight shipments often need to be palletized, which means products are grouped together on pallets for more efficient transportation.Delivery Speed
Shipping is typically faster, especially when express options are chosen. Freight, while sometimes slower, can also offer expedited services, though at a premium cost. When delivery speed is not the most critical factor, businesses often choose freight due to the cost savings.Flexibility of Transportation
Shipping relies on fewer transportation modes, primarily using ground transport or air for small packages. Freight offers much more flexibility with its use of sea, rail, air, and truck options. The mode chosen for freight will often depend on cost, distance, and the nature of the goods being transported.5. When to Choose Shipping vs Freight
Making the right choice between shipping and freight depends on several factors, primarily the size, weight, and urgency of the shipment.When to Choose Shipping:
You’re sending smaller parcels that weigh under 150 pounds.Delivery speed is crucial, and you need express options such as overnight or two-day shipping.
The shipment is a personal or e-commerce order, where fast and reliable service is essential.
When to Choose Freight:
You’re moving large quantities of goods, especially over 150 pounds or bulky shipments that are palletized or containerized.Cost efficiency is more important than speed, especially for international or bulk shipments.
You need to coordinate complex logistics, and the shipment requires multiple modes of transport, like air, sea, and ground.
6. FAQs
1. What is the key difference between shipping and freight?
The main difference between shipping and freight is the size and weight of the goods being transported. Shipping typically refers to smaller packages under 150 pounds, while freight handles large, heavy, or bulk shipments.2. When should you choose freight over shipping?
Choose freight over shipping when you are transporting large or heavy goods, especially when the shipment exceeds 150 pounds. Freight services are also more cost-effective for large quantities and bulk shipments.3. Is shipping cheaper than freight?
For smaller packages, shipping can be more expensive on a per-unit weight basis. Freight becomes the more cost-effective option when you’re dealing with large-scale shipments, as it offers lower costs per unit of weight.4. What is the most efficient mode for large-scale transport?
For long-distance and international transport, sea freight is often the most cost-efficient, especially for non-urgent goods. However, air freight is faster but more expensive.5. Can small businesses use freight services?
Yes, small businesses can use freight services, particularly if they need to move large quantities of products, raw materials, or equipment. Freight services can be scaled to suit the needs of businesses, regardless of size. Post Views:5279
Post Views:5279
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
7 Key Strategies to Reduce Shipping Costs
Next Post
TAGS
Hot Research
Get Custom eCommerce Fulfillment Service
Book a Meeting
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.




 TAGS:
TAGS: