Table of Contents
Top 10 Warehouse Management Challenges and Solutions
Time: Oct 11,2024 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
Warehouses are the backbone of the supply chain, but managing warehouses efficiently is no easy task. Many businesses struggle with common issues like inventory discrepancies, space optimization, and labor productivity.In this blog post, we’ll discuss the top 10 warehouse management challenges and practical solutions that can help your business boost efficiency, reduce errors, and improve overall performance. Whether you’re dealing with order delays or reverse logistics, these insights will help you streamline your operations for better results.

Challenge 1: Inefficient Warehouse Layout and Space Utilization
Inefficient warehouse layout and poor space utilization are major warehouse management challenges because they increase operational costs, reduce productivity, and create safety risks. A poorly designed layout leads to longer travel times for workers, inefficient use of space, and difficulty locating inventory, all of which slow down order fulfillment and can cause errors. Additionally, it limits the ability to scale operations and integrate automation. The inefficiencies raise costs and impact customer satisfaction by delaying shipments and increasing the likelihood of errors.Solution: Streamlining Warehouse Layout for Optimized Efficiency
Optimized Layout Design: Design the warehouse layout to minimize travel times by organizing items based on demand frequency (e.g., placing high-demand items closer to picking and packing areas). Implement clear pathways for easy movement of personnel and equipment.Vertical Space Utilization: Make better use of vertical storage space with the use of racks, shelves, and mezzanines, ensuring that every cubic foot is optimized. It can help avoid overcrowding at floor level and make room for additional inventory without expanding the warehouse footprint.
Slotting Optimization: Use slotting techniques to assign products to storage locations based on size, weight, and order frequency. It allows for efficient picking and replenishment, reducing unnecessary movement and improving flow.
Technology and Automation: Implement warehouse management systems (WMS) to track inventory in real-time, improving space allocation and enabling efficient use of storage areas. Additionally, consider automation solutions like conveyors, robotic pickers, or automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) to streamline movement and improve space utilization.
Regular Audits and Reconfiguration: Periodically review and audit warehouse layout and space utilization to identify inefficiencies and adjust the layout or storage strategies to meet changing inventory and demand patterns.
Challenge 2: Poor Inventory Management

Poor inventory management is a significant warehouse management challenge because it leads to stock discrepancies, inefficient operations, and higher costs. Without proper tracking, items can be misplaced, leading to stockouts, overstocking, or lost products, which disrupts order fulfillment and reduces customer satisfaction. It also results in wasted storage space and can increase labor costs due to time spent searching for items. Poor inventory control hampers accurate forecasting and reordering, making it difficult to maintain the right stock levels and meet customer demand, ultimately affecting profitability.
Solution: Implementing Real-Time Inventory Tracking Systems
Adopt a Warehouse Management System: Use a WMS to automate inventory tracking, providing real-time data on stock levels, locations, and movement. It ensures accurate and up-to-date information, reducing errors and improving stock control.Use Barcode or RFID Technology: Implement barcode or RFID scanning for tracking inventory movement. Technology helps with real-time updates, reduces human errors during picking or replenishment, and speeds up the inventory counting process.
Establish Inventory Control Methods: Utilize methods like FIFO (First In, First Out) or LIFO (Last In, First Out) to ensure proper stock rotation and prevent issues like product expiration or obsolescence.
Regular Audits and Cycle Counting: Conduct regular inventory audits and cycle counts to verify stock levels and identify discrepancies. It ensures ongoing accuracy without having to shut down operations for a full physical inventory.
Implement Demand Forecasting: Use data analytics and historical sales information to forecast demand accurately, ensuring optimal stock levels. It prevents overstocking and stockouts while improving order fulfillment efficiency.
Optimize Reordering Processes: Set up automated reordering alerts or thresholds within your WMS to maintain ideal stock levels, minimizing the risk of running out of critical products.
Challenge 3: Managing Shipping and Delivery Challenges

Without proper systems to streamline packing, labeling, and carrier management, warehouses may experience bottlenecks in shipping, leading to missed delivery deadlines. Inaccurate shipping processes can cause returns, increased operational costs, and damage to the company's reputation. These challenges ultimately affect profitability and customer trust.
Solution: Optimizing Last-Mile Delivery Solutions
Implement a Transportation Management System (TMS): A TMS helps optimize shipping routes, select the most cost-effective carriers, and provide real-time tracking of shipments. It increases efficiency and reduces delays and costs associated with transportation.Integrate Warehouse Management with Shipping: Integrating the Warehouse Management System with shipping systems enables seamless order processing, from picking and packing to labeling and dispatching. It reduces errors, streamlines workflows, and speeds up the shipping process.
Automate Labeling and Documentation: Automating the creation of shipping labels and necessary documentation ensures accuracy and reduces the time spent on manual processes, minimizing the risk of delays or mistakes.
Use Real-time Tracking and Visibility Tools: Providing customers and warehouse teams with real-time tracking information improves visibility, enhances communication with carriers, and helps manage expectations. It also allows proactive resolution of any shipping delays.
Optimize Carrier Relationships and Contracts: Regularly review carrier performance and negotiate contracts to ensure that the best rates and service levels are achieved. Multi-carrier strategies can also help prevent reliance on a single provider and mitigate delays.
Efficient Packing and Order Prioritization: Organize packing stations to streamline the packaging process and use prioritization methods to handle urgent orders first. It ensures that high-priority shipments are processed and delivered on time.
Challenge 4: Managing Seasonal Demand Fluctuations
Without proper forecasting and flexible planning, these fluctuations can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and poor customer service. Balancing resources effectively during these shifts is crucial to maintaining smooth operations and meeting customer expectations throughout the year.
Solution: Forecasting and Planning for Seasonality
Accurate Demand Forecasting: Use historical sales data, market trends, and predictive analytics to anticipate seasonal demand changes. Accurate forecasting helps warehouses prepare the right amount of inventory and allocate resources in advance of peak seasons.Scalable Workforce Management: Implement flexible staffing solutions, such as hiring temporary workers during peak periods or cross-training employees to handle multiple roles. It ensures that the warehouse can scale its workforce according to demand without incurring excessive labor costs in low-demand periods.
Optimize Inventory Levels: Adopt dynamic inventory management strategies like Just-in-Time (JIT) or safety stock levels to avoid overstocking during low-demand periods while ensuring sufficient stock during peaks. Proper stock rotation methods like FIFO (First In, First Out) can also help prevent product obsolescence.
Adjust Storage Layouts and Space: Reconfigure warehouse layouts temporarily during peak seasons to accommodate higher volumes of fast-moving items in more accessible locations. This helps improve efficiency in picking, packing, and shipping during demand spikes.
Leverage Technology for Automation: Use Warehouse Management Systems and automation technologies such as conveyor belts, robotics, and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) to increase operational efficiency and manage high order volumes during busy periods.
Collaborate with Suppliers and Carriers: Maintain open communication with suppliers and carriers to ensure they can meet your fluctuating inventory and shipping needs. Establish contingency plans for quick replenishment or transportation adjustments during peak seasons.
Challenge 5: Labor Management and Workforce Productivity

The shift toward automation may create concerns about job security, necessitating careful management of workforce morale and skill development. Successfully integrating automation while upskilling employees is crucial to maintaining a high-performing warehouse operation.
Solution: Training and Automation for Enhanced Workforce Efficiency
Comprehensive Training Programs: Implement structured training programs to ensure employees are well-equipped to use new technologies. This includes hands-on training with automated systems, software tools, and safety protocols. Regular refresher courses should also be provided to keep skills up to date as technology evolves.Phased Automation Rollout: Introduce automation in stages rather than all at once, allowing employees to gradually adapt to changes. This reduces disruptions and gives workers time to adjust their workflows around new systems, leading to smoother transitions and improved operational efficiency.
Upskilling and Cross-training: Invest in upskilling employees to handle more technical roles, such as operating, maintaining, or troubleshooting automated systems. Cross-training workers in multiple areas of warehouse operations also improves flexibility, enabling employees to cover different roles as needed, particularly in response to fluctuating demand.
Fostering a Culture of Adaptability: Encourage a growth mindset within the workforce by promoting continuous learning and emphasizing the benefits of automation, such as reduced manual labor and increased operational efficiency. Address concerns about job security by highlighting new opportunities for career development and skill advancement.
Integration of Human and Machine Workflows: Design workflows that effectively combine human and automated processes. For example, automation can handle repetitive tasks like sorting or transportation, while employees focus on more complex tasks like quality control or exception management, creating a balanced and efficient operation.
Challenge 6: Picking and Packing Efficiency
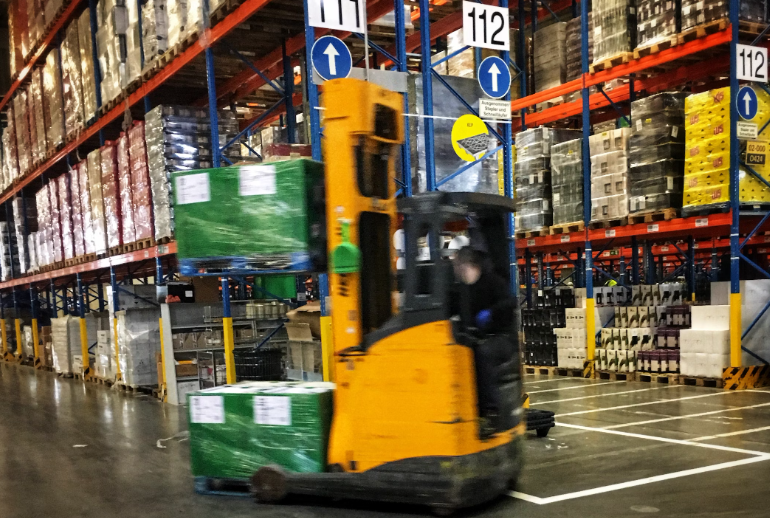

The inefficiencies can cause delays in shipping, affecting customer satisfaction, and may require rework or returns, further adding to operational costs. Optimizing these workflows is crucial to maintaining high productivity, reducing errors, and meeting customer expectations for fast, accurate deliveries.
Solution: Leveraging Warehouse Automation Tools
Use a Warehouse Management System: A WMS helps streamline picking by organizing orders efficiently, guiding workers to the right locations, and prioritizing tasks. It can also integrate with mobile devices for real-time updates, reducing errors and speeding up order processing.Implement Zone and Batch Picking: Use picking strategies like zone picking, where workers focus on specific areas, or batch picking, which allows multiple orders to be picked simultaneously. These methods reduce travel time and increase productivity.
Optimize Warehouse Layout: Arrange items based on frequency of use, placing high-demand products closer to picking and packing areas. It reduces the time it takes to locate and retrieve items, improving overall speed and efficiency.
Invest in Automation Tools: Use automated systems like conveyor belts, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), or robotic pickers to handle repetitive tasks, reducing manual labor and increasing picking speed.
Standardize Packing Processes: Create standardized packing procedures, ensuring consistent and efficient packing practices. Implementing automated packaging machines for commonly sized orders can also save time and reduce errors.
Train and Cross-train Staff: Provide employees with proper training on picking and packing techniques and cross-train them in multiple roles. It ensures flexibility during peak times and reduces dependency on specific individuals.
Challenge 7: Managing Returns and Reverse Logistics
Managing returns and reverse logistics is a major warehouse management challenge because it requires handling returned items efficiently while minimizing costs and ensuring proper inventory management. The process involves inspecting returned goods, restocking sellable items, disposing of damaged products, and managing refunds or exchanges. Poorly managed returns can lead to increased operational costs, inventory inaccuracies, and delays in reselling items.Reverse logistics adds complexity to warehouse operations by requiring separate workflows for processing returns, which can disrupt the efficiency of regular outbound shipments. A streamlined, cost-effective returns process is essential to maintaining customer satisfaction and controlling operational expenses.
Solution: Creating a Structured Returns Process
Develop a Clear Returns Policy: Establish a well-defined returns policy that is easy for customers to follow and for the warehouse team to execute. It helps minimize unnecessary returns and streamlines the process for both parties.Use a Warehouse Management System for Reverse Logistics: A WMS can automate and streamline the returns process by tracking returned items, automating restocking, and managing workflows for inspection and processing. It helps ensure accurate inventory records and reduces manual handling errors.
Create Dedicated Return Areas: Designate specific areas within the warehouse for handling returned goods. It prevents interference with regular outbound operations and ensures that returned items are processed efficiently.
Establish Standardized Inspection and Restocking Procedures: Implement a consistent process for inspecting returned items to determine whether they can be restocked, refurbished, or disposed of. Clear guidelines ensure quicker decisions on whether to return the item to inventory, minimizing delays.
Leverage Automation: Use automation tools such as barcode scanning or RFID technology to streamline the tracking, inspection, and restocking of returned goods. It reduces manual tasks and speeds up the process, helping to manage high volumes of returns during peak seasons.
Partner with Reverse Logistics Providers: For complex reverse logistics, partnering with third-party reverse logistics providers can help handle the process more efficiently, especially for international returns or items requiring special handling.
Analyze Return Data: Regularly analyze return data to identify common reasons for returns and take proactive steps to reduce them, such as improving product descriptions or quality control. This can help reduce the volume of returns over time.
Challenge 8: Handling Safety and Compliance Issues
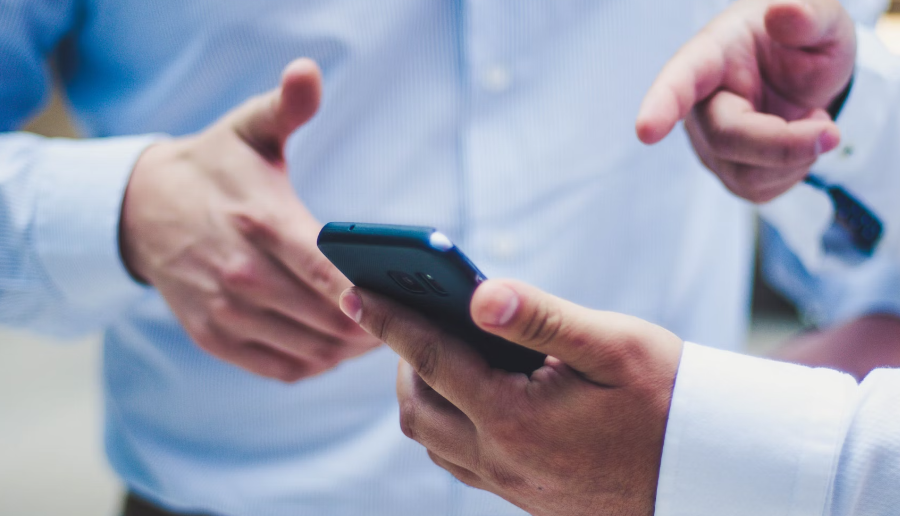

Warehouses must comply with safety regulations related to fire hazards, hazardous materials, and worker protection. Failure to manage these effectively can lead to accidents, legal penalties, and operational disruptions, making robust safety protocols and regulatory adherence essential for smooth and secure operations.
Solution: Implementing Safety Protocols and Training
Develop and Enforce Safety Protocols: Establish clear, detailed safety procedures that cover all aspects of warehouse operations, such as equipment handling, hazard management, and emergency response. Ensure these protocols are well-documented and consistently enforced.Comprehensive Employee Training: Provide regular safety training for all employees, including new hires and temporary workers. It should cover safe handling practices, equipment operation, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses help maintain awareness and adherence to safety standards.
Implement Safety Audits and Inspections: Conduct regular safety audits and inspections to identify potential hazards, such as obstructed pathways, faulty equipment, or improper storage of hazardous materials. Address issues immediately to prevent accidents and ensure compliance.
Use Safety Technology: Leverage technology such as wearable devices, automated monitoring systems, or sensors to detect potential risks, track worker movement, and prevent accidents in real-time. Additionally, warehouse management systems can be used to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations: Stay updated on local and industry-specific safety regulations and standards, and ensure your warehouse complies with them. Designate a compliance officer or team to regularly review and update policies in line with regulatory changes.
Promote a Safety-First Culture: Foster a workplace culture that prioritizes safety, encouraging workers to report hazards or unsafe conditions without fear of repercussions. Recognize and reward adherence to safety protocols to reinforce their importance.
Challenge 9: Integrating Warehouse Management Systems

Solution: Enhancing Picking Strategies and Technology
Conduct a Thorough Assessment: Start by evaluating your warehouse operations to identify your specific needs. Choose a WMS that aligns with your business requirements and can grow as your business expands.Select the Right Integration Partner: Work with an experienced WMS provider or integration specialist who understands your industry. A knowledgeable partner can help ensure a smooth implementation and resolve technical issues efficiently.
Implement in Phases: Roll out the WMS in stages, beginning with a pilot test in one area before scaling up. This allows you to troubleshoot and refine processes, minimizing disruptions during full implementation.
Ensure Compatibility: Make sure the WMS integrates seamlessly with other systems like ERP, TMS, or CRM. Use APIs or middleware to streamline the integration and ensure smooth data flow between systems.
Train Your Team: Provide comprehensive training for all employees who will use the WMS. This helps them get comfortable with the new system, reduces resistance to change, and boosts efficiency.
Cleanse and Standardize Data: Before integration, ensure all data—such as inventory and supplier information—is accurate and standardized to prevent errors during the transition.
Offer Ongoing Support: After the WMS is up and running, provide continuous support and monitor system performance. Regular reviews and improvements ensure the system stays aligned with your operational needs.
Challenge 10: Order Accuracy and Timely Fulfillment
Order accuracy and timely fulfillment are key warehouse management challenges because they directly affect customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Inaccurate orders, such as picking the wrong items or incorrect quantities, can lead to returns, customer complaints, and additional handling costs. Meanwhile, delays in fulfilling orders can result in missed deadlines, damaged relationships with customers, and negative impacts on the company's reputation.Maintaining high levels of accuracy and speed in order processing requires well-organized systems, efficient workflows, and a well-trained workforce, all of which can be difficult to achieve consistently, especially during peak demand periods.
Solution: Enhancing Picking Strategies and Technology
Implement a Warehouse Management System: A WMS helps track inventory in real-time and guides workers through optimized picking processes, reducing human errors and ensuring accurate order fulfillment. It also streamlines order processing to speed up fulfillment.Adopt Barcode or RFID Scanning: Using barcode or RFID scanning technology during picking and packing ensures that the correct items are selected and packed, reducing the likelihood of mistakes and improving accuracy.
Use Batch or Zone Picking Strategies: Organize picking workflows with methods like batch picking (multiple orders at once) or zone picking (workers assigned to specific areas), which minimize travel time and improve efficiency, leading to faster order fulfillment.
Cross-Train Employees: Train staff in multiple roles within the warehouse to create flexibility, allowing you to reallocate resources to high-demand areas when necessary. It ensures consistent performance even during peak times.
Establish Quality Control Procedures: Implement a final check or audit system before orders are shipped to verify accuracy and catch any errors before products leave the warehouse, ensuring that only correct and complete orders reach customers.
Utilize Data for Continuous Improvement: Regularly analyze order accuracy and fulfillment speed metrics to identify bottlenecks or recurring errors. Use this data to refine processes and address inefficiencies proactively.
FAQs
1. What is the most common warehouse management challenge?
The most common challenge is inefficient space utilization, leading to bottlenecks in workflow and increased costs.2. How can technology improve warehouse management?
Technology like WMS, real-time inventory tracking, and automation tools can enhance accuracy, efficiency, and visibility in warehouse operations.3. How can we improve order accuracy in a warehouse?
Use technology like barcode scanning, voice-picking systems, and real-time analytics to track order accuracy and reduce errors.4. What is reverse logistics in warehouse management?
Reverse logistics refers to the process of handling returns, repairs, and recycling of products from the customer back to the warehouse.5. How do you manage labor shortages in a warehouse?
Cross-train employees, implement automation tools, and use labor management software to optimize workforce productivity. Post Views:2435
Post Views:2435
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
Indiegogo Failures: What Happens Next and How to Bounce Back Stronger
Next Post
3PL vs In-house Logistics: Why You Should Consider Third-party Logistics
TAGS
Hot Research
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.




 TAGS:
TAGS: