Table of Contents
What Does ARO Mean in Shipping?
Time: Apr 10,2025 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
Shipping contracts and supply chain agreements are full of technical terms, and one that often causes confusion is ARO—After Receipt of Order. It may sound simple, but understanding exactly what this term means can help both buyers and sellers avoid miscommunication and financial pitfalls. In this guide, we’ll explore the definition of ARO in shipping, why it matters, and how it compares to other common payment terms like ARP and COD.
1. What Is ARO (After Receipt of Order)?
After Receipt of Order (ARO) is a payment term indicating that the countdown for payment due dates begins once the seller acknowledges receipt of an order from the buyer. For instance, if the agreed term is "ARO 15 days," the buyer is expected to complete the payment within 15 days following the seller's confirmation of the order.ARO is integral in defining clear timelines for financial transactions, ensuring both parties have a mutual understanding of payment schedules. It helps in setting expectations and mitigating potential disputes related to payment delays.
2. What Does ARO Mean in Shipping?
In the shipping sector, ARO plays a pivotal role in dictating when payments are due in relation to the order process. Unlike terms that tie payment deadlines to the shipment or delivery dates, ARO focuses on the order acknowledgment date. It means that the payment period starts immediately after the seller confirms the order, regardless of when the goods are shipped or delivered.For example, consider a scenario where a buyer places an order on March 1st, and the seller acknowledges it on the same day. If the payment term is "ARO 30 days," the buyer is obligated to make the payment by March 31st, even if the shipment occurs at a later date.
3. Importance of ARO in Buyer-Seller Agreements
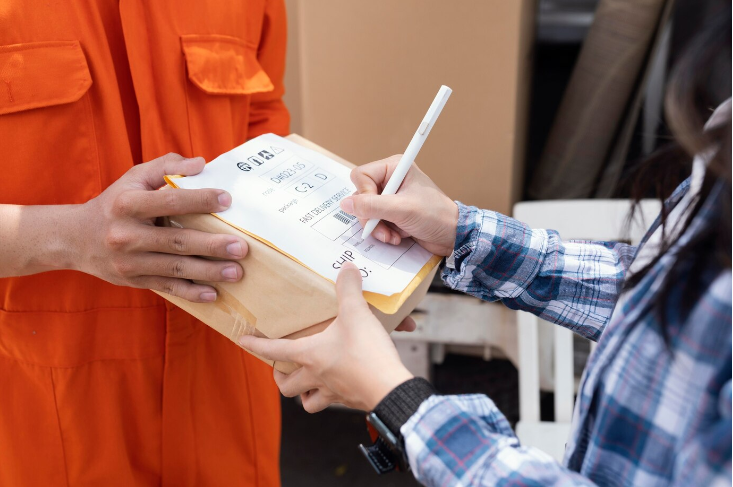

- Clarity in Payment Schedules: ARO establishes a clear timeline for payments, reducing ambiguities that can lead to disputes.
- Cash Flow Management: For sellers, knowing when to expect payments aids in better financial planning and cash flow management.
- Trust Building: ARO terms can foster trust, especially in long-term business relationships, by demonstrating a commitment to timely payments.
However, it's essential for both parties to agree on ARO terms that align with their operational capabilities and financial strategies to avoid potential cash flow mismatches.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of ARO
While ARO terms offer several advantages, they also come with certain drawbacks. Understanding these can help businesses make informed decisions when negotiating payment terms.Advantages
- Predictable Financial Planning: ARO provides a set schedule for payments, aiding in budgeting and financial forecasting.- Reduced Payment Disputes: Clearly defined payment timelines minimize misunderstandings and disputes over payment schedules.
- Improved Vendor Relationships: Adhering to ARO terms demonstrates professionalism and reliability, fostering stronger relationships with suppliers and partners.
Disadvantages
- Potential Payment Delays: Since payment is due after the order is received, sellers may experience delays in receiving funds, impacting their cash flow.- Cash Flow Challenges for Sellers: Extended payment windows can pose cash flow challenges for sellers, especially if they rely on prompt payments to fund operations.
- Complex Tracking: Managing multiple orders with different ARO timelines can become complicated, potentially leading to errors in payment tracking.
5. ARO vs Other Payment Terms
It's essential to distinguish ARO from other common payment terms to select the most suitable arrangement for a business transaction.|
Payment Term |
Definition | Payment Timing | Best Suited For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After Receipt of Order (ARO) | Payment is due a specified number of days after the seller receives the buyer's order. | Payment is made within the agreed timeframe after the seller acknowledges the order, possibly before shipment. |
Established business relationships with mutual trust. | Requires clear communication; potential cash flow implications if payment is delayed. |
| After Receipt of Payment (ARP) | Seller ships goods only after receiving full payment from the buyer. |
Payment is made upfront before any goods are shipped. | High-risk transactions or new business relationships. | Protects sellers from non-payment; may delay shipment commencement. |
| Net Payment Terms | Payment is due a certain number of days after the invoice date. | Payment is made within the specified period post-invoice issuance, regardless of order or shipping dates. |
Routine transactions with regular clients. | Standard in many industries; facilitates predictable cash flow. |
| Cash on Delivery (COD) | Buyer pays for goods at the time of delivery. | Payment is made when the goods are delivered to the buyer. | E-commerce and retail transactions. | Reduces buyer's risk; sellers face potential non-acceptance of goods upon delivery. |
6. Implementing ARO in Business Operations
When considering the adoption of ARO terms, businesses should evaluate their relationships with trading partners and their cash flow positions. ARO is most suitable for long-term partnerships where trust has been established. Clear communication of payment expectations and timelines is crucial to avoid misunderstandings.Additionally, businesses should have systems in place to track orders and payments effectively, ensuring that ARO terms are adhered to and that cash flow remains stable.
7. Conclusion
In the realm of shipping and logistics, understanding and implementing appropriate payment terms like After Receipt of Order (ARO) is vital for smooth operations and robust financial management. While ARO offers benefits such as clear payment timelines and enhanced cash flow management, it also presents challenges like potential payment delays and complex tracking. By carefully evaluating the advantages and disadvantages, and comparing ARO with other payment terms, businesses can make informed decisions that best suit their operational needs and foster strong, trustworthy relationships with their partners.8. FAQs
1. What does ARO stand for in shipping?
ARO stands for After Receipt of Order, indicating that payment is due a specified number of days after the seller receives the buyer's order.2. How does ARO differ from ARP?
ARO requires payment after the seller receives the order, while ARP mandates that payment be made before the seller ships the goods.3. Is ARO suitable for new business relationships?
ARO is typically recommended for long-term partnerships with established trust, as it involves the seller initiating fulfillment before receiving payment.4. Can ARO terms affect a seller's cash flow?
Yes, since payment is received after order fulfillment begins, sellers may experience delays in funds, potentially impacting cash flow.5. How can businesses manage multiple ARO timelines effectively?
Implementing robust tracking systems and clear communication channels can help businesses monitor various ARO timelines and ensure timely payments. Post Views:175
Post Views:175
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
Digital Logistics vs. Traditional Logistics: A Comprehensive Comparison
Next Post
A Complete Guide to Standard Shipping: Timeframes, Costs, and Best Carriers
TAGS
Hot Research
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.




 TAGS:
TAGS: