Table of Contents
What Is Inventory Management
Time: Jun 25,2024 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
Efficient inventory management is vital for the success of any business, affecting cost control and customer satisfaction. From small retailers to large manufacturers, effectively managing inventory can make a significant difference.
This blog article provides a thorough understanding of inventory management, offering actionable strategies to maintain optimal stock levels. Through exploring various techniques, tools, and best practices, you'll learn how to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall business performance.

1. Understanding Inventory
Inventory is the lifeblood of businesses in industries ranging from retail to manufacturing. It encompasses all the goods and materials a company holds for the purpose of resale, production, or use in day-to-day operations. Inventory typically includes raw materials, components, and finished products. Inventory management is a strategic approach to managing these resources efficiently, ensuring that the right amount of inventory is available at the right time, and in the right place.
Companies often use sophisticated inventory management systems to track inventory levels in real-time. There are three primary methods of accounting for inventory:
Companies often use sophisticated inventory management systems to track inventory levels in real-time. There are three primary methods of accounting for inventory:
First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Costing: The oldest inventory items are recorded as sold first.
Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) Costing: The most recently acquired inventory items are recorded as sold first.
Weighted-Average Costing: The cost of goods available for sale is divided by the number of units available for sale to determine an average cost per unit.
An inventory account typically consists of four categories:
Raw Materials: Various materials purchased for the production process, which must undergo significant work to be transformed into finished goods.
Work in Process (Goods-in-Process): Raw materials currently being transformed into finished products.
Finished Goods: Completed products ready for sale to customers.
Merchandise: Finished goods purchased from a supplier for future resale.
2. What Is Inventory Management

Inventory management is the process of efficiently overseeing, controlling, and organizing a company's inventory of goods. Inventory management includes ensuring that there is an adequate supply to meet customer demand while minimizing excess stock that can tie up capital. Key aspects of inventory management include:
Tracking Inventory Levels: Monitoring the quantity of raw materials, work-in-process, and finished goods in real-time using sophisticated inventory management systems.
Accounting Methods: Employing methods such as First-In-First-Out (FIFO), Last-In-First-Out (LIFO), and Weighted-Average Costing to value and manage inventory costs.
Physical Counting: Regularly counting and measuring inventory to ensure accuracy in records and balance sheets.
Accounting Methods: Employing methods such as First-In-First-Out (FIFO), Last-In-First-Out (LIFO), and Weighted-Average Costing to value and manage inventory costs.
Physical Counting: Regularly counting and measuring inventory to ensure accuracy in records and balance sheets.
Key Objectives of Inventory Management
Ensuring Product Availability: Ensuring that products are available when customers need them.
Minimizing Holding Costs: Reducing the costs associated with storing and managing inventory.
Optimizing Order Quantity: Balancing order quantities to avoid excess stock and stockouts.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: Providing timely delivery of products to customers.
Minimizing Holding Costs: Reducing the costs associated with storing and managing inventory.
Optimizing Order Quantity: Balancing order quantities to avoid excess stock and stockouts.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: Providing timely delivery of products to customers.
3. Methods of Inventory Management
Various inventory management methods are employed by companies based on the type of business or product they deal with. The four most common methods include just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, materials requirement planning (MRP), economic order quantity (EOQ), and days sales of inventory (DSI), among others.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-In-Time (JIT) is a strategy where materials are ordered and received only as they are needed in the production process. JIT minimizes inventory costs but requires precise coordination with suppliers to avoid production delays.
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP)
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Its primary goal is to ensure that materials are available for production and products are available for delivery to customers, while minimizing inventory levels and optimizing production efficiency. MRP helps in planning and controlling the inventory, ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time in the right quantities.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a formula used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes the total cost of inventory, including ordering and holding costs. EOQ helps in achieving the most cost-efficient inventory levels.
Days Sales of Inventory (DSI)
Days Sales of Inventory (DSI) is a financial metric that indicates the average number of days a company takes to sell its entire inventory during a specific period. It is used to assess the efficiency of inventory management and to determine how quickly a company can convert its inventory into sales. Lower DSI values typically indicate more efficient inventory management, while higher values may suggest overstocking or slower-moving inventory.
The formula to calculate DSI is:
DSI=(Average Inventory/Cost of Goods Sold)×365
Where:
Average Inventory is the average value of inventory over the period being analyzed.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the total cost of producing or purchasing the goods that were sold during the period.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the total cost of producing or purchasing the goods that were sold during the period.
4. How Does Inventory Management Work
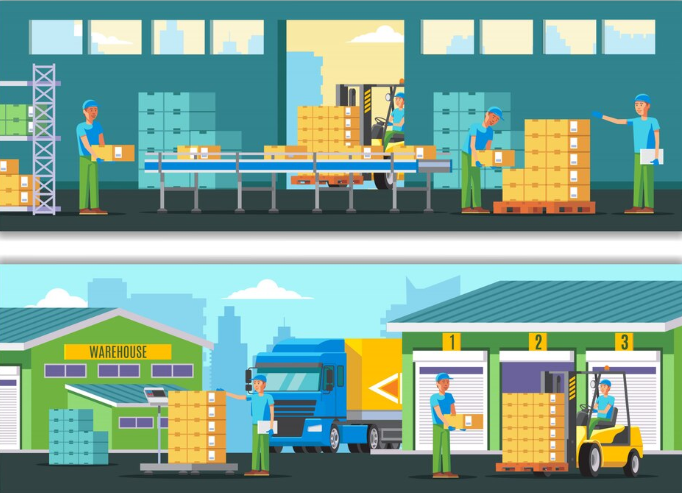
Inventory management works by implementing a set of policies, procedures, and technologies to monitor and control inventory levels. Key components include:
Demand Forecasting: Predicting future customer demand based on historical data and market trends.
Inventory Ordering: Determining the optimal order quantities and timing to replenish inventory.
Inventory Storage: Storing inventory in a manner that maximizes space utilization and accessibility.
Inventory Tracking: Monitoring inventory levels in real-time to ensure accuracy and prevent stockouts or excess stock.
Inventory Analysis: Analyzing inventory data to identify trends, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Inventory Ordering: Determining the optimal order quantities and timing to replenish inventory.
Inventory Storage: Storing inventory in a manner that maximizes space utilization and accessibility.
Inventory Tracking: Monitoring inventory levels in real-time to ensure accuracy and prevent stockouts or excess stock.
Inventory Analysis: Analyzing inventory data to identify trends, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Technologies such as inventory management software and automated systems play a critical role in modern inventory management, providing real-time data and analytics to optimize inventory processes.
5. Why Is Inventory Management Important
Inventory management is a vital aspect of any business that involves the sale of physical goods.
Cost Optimization
One of the primary reasons for its importance is cost optimization. Efficient inventory management ensures that a company minimizes the costs associated with holding inventory, such as storage, insurance, and taxes. It also helps avoid the expenses linked to overstocking or stockouts. Overstocking can lead to increased storage costs and potential losses from unsold goods, while stockouts can result in lost sales and dissatisfied customers.
Improved Cash Flow
Another significant benefit of effective inventory management is improved cash flow. By managing inventory levels carefully, companies can ensure they do not tie up too much capital in unsold goods. Efficient inventory management frees up resources that can be used elsewhere in the business, such as for investment in growth opportunities or to cover operational expenses. Good inventory management practices help maintain a healthy balance between supply and demand, which is essential for financial stability.
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is also greatly enhanced through proper inventory management. When companies maintain optimal inventory levels, they can ensure that products are available when customers need them. It reduces lead times and the likelihood of backorders, which can frustrate customers and drive them to competitors. By consistently meeting customer demand, businesses can build trust and loyalty, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
Enhanced Efficiency
Effective inventory management greatly improves efficiency. Streamlining inventory procedures allows companies to better align production schedules, order processing, and supply chain operations. Efficient inventory management leads to higher productivity and reduces waste and obsolescence, crucial for perishable or trend-dependent products.
Accurate Financial Report
Accurate financial reporting is crucial for any business, and inventory management plays a significant role in this. Precise inventory records are essential for producing reliable financial statements, which are important for internal decision-making and for meeting the expectations of external stakeholders like investors and regulators. Moreover, the insights gained from inventory data can support strategic planning, informing decisions related to product development, marketing strategies, and expansion efforts.
Risk Management
Lastly, inventory management is integral to risk management. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, companies can better navigate supply chain disruptions, demand fluctuations, and economic uncertainties. This proactive approach helps businesses remain resilient and adaptable in the face of challenges, ensuring long-term sustainability and success. In summary, inventory management is a cornerstone of effective business operations, contributing to cost control, improved customer service, and enhanced profitability.
6. Inventory Management vs Inventory Control
While often used interchangeably, inventory management and inventory control are distinct concepts:
Inventory Management
Inventory management encompasses the overall process of managing inventory levels and supply chain operations. It includes demand forecasting, inventory ordering, storage, tracking, and analysis. The goal is to maintain optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand and minimize costs.
Inventory Control
Inventory control focuses specifically on maintaining the correct inventory levels to meet demand. It involves activities such as stock rotation, cycle counting, and tracking inventory transactions to ensure accuracy and prevent losses. Inventory control is a subset of inventory management.
7. What Are the Signs of Efficient Inventory Management

Efficient inventory management can be identified through several key indicators:
Low Inventory Holding Costs: Efficient inventory management keeps storage costs, insurance, and taxes low by avoiding overstocking and maintaining optimal inventory levels.
High Inventory Turnover Rate: A high turnover rate indicates that inventory is moving quickly through the supply chain, reflecting strong sales and effective stock management.
Minimal Stockouts: Efficient inventory management ensures that products are available when customers need them, minimizing the occurrence of stockouts and lost sales opportunities.
Reduced Obsolescence and Waste: Effective management helps avoid overstocking of items that may become obsolete or spoil, thereby reducing waste and associated costs.
Accurate Inventory Records: Reliable and up-to-date inventory records reflect a well-managed inventory system, aiding in precise financial reporting and decision-making.
Improved Cash Flow: By maintaining optimal inventory levels, companies can free up capital that would otherwise be tied up in unsold stock, leading to better cash flow.
Satisfied Customers: Efficient inventory management ensures that customer demand is met promptly, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Effective Use of Technology: Utilizing advanced inventory management systems and tools indicates an efficient inventory process, allowing for real-time tracking and better forecasting.
Balanced Inventory Levels: Maintaining the right balance between too much and too little inventory reflects efficient inventory management, reducing the risks of both overstocking and stockouts.
Streamlined Operations: Efficient inventory management contributes to smoother operations, with well-coordinated production schedules, order fulfillment, and supply chain activities.
Low Inventory Holding Costs: Efficient inventory management keeps storage costs, insurance, and taxes low by avoiding overstocking and maintaining optimal inventory levels.
High Inventory Turnover Rate: A high turnover rate indicates that inventory is moving quickly through the supply chain, reflecting strong sales and effective stock management.
Minimal Stockouts: Efficient inventory management ensures that products are available when customers need them, minimizing the occurrence of stockouts and lost sales opportunities.
Reduced Obsolescence and Waste: Effective management helps avoid overstocking of items that may become obsolete or spoil, thereby reducing waste and associated costs.
Accurate Inventory Records: Reliable and up-to-date inventory records reflect a well-managed inventory system, aiding in precise financial reporting and decision-making.
Improved Cash Flow: By maintaining optimal inventory levels, companies can free up capital that would otherwise be tied up in unsold stock, leading to better cash flow.
Satisfied Customers: Efficient inventory management ensures that customer demand is met promptly, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Effective Use of Technology: Utilizing advanced inventory management systems and tools indicates an efficient inventory process, allowing for real-time tracking and better forecasting.
Balanced Inventory Levels: Maintaining the right balance between too much and too little inventory reflects efficient inventory management, reducing the risks of both overstocking and stockouts.
Streamlined Operations: Efficient inventory management contributes to smoother operations, with well-coordinated production schedules, order fulfillment, and supply chain activities.
8. How to Optimize Inventory Management
Optimizing inventory management involves implementing best practices and leveraging technology to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Implement Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software provides real-time data and analytics, automates inventory processes, and helps businesses maintain optimal inventory levels. Features to look for include demand forecasting, order management, and inventory tracking.
Forecast Demand Accurately
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for maintaining optimal inventory levels. Use historical data, market analysis, and advanced forecasting techniques to predict future demand. This helps in making informed decisions about inventory replenishment.
Optimize Order Quantity and Timing
Use methods like EOQ and JIT to determine the best order quantities and timing. This ensures that inventory levels are aligned with demand, reducing holding and ordering costs.
Regularly Review and Adjust Inventory Levels
Continuously monitor inventory performance and make necessary adjustments. Regular reviews help identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. Implement cycle counting and periodic audits to ensure inventory accuracy.
Train Staff
Ensure that employees are knowledgeable about inventory management practices and software. Provide training on inventory management systems, best practices, and the importance of accurate inventory tracking. Well-trained staff can effectively manage inventory and identify potential issues before they become problems.
Leverage Automation
Automate routine inventory management tasks to reduce errors and increase efficiency. Automated systems can handle tasks such as inventory tracking, reordering, and reporting, freeing up staff to focus on more strategic activities.
Optimize Warehouse Layout
Design your warehouse layout to maximize space utilization and improve accessibility. Implementing an efficient layout reduces the time and effort required to locate and retrieve items, improving overall operational efficiency.
Improve Supplier Relationships
Develop strong relationships with suppliers to ensure reliable and timely deliveries. Collaborate with suppliers to improve lead times, reduce order quantities, and negotiate better terms. Strong supplier relationships contribute to a more efficient and resilient supply chain.
Implement Inventory Optimization Techniques
Use techniques such as ABC analysis, safety stock, and reorder point calculations to optimize inventory levels. These techniques help prioritize inventory management efforts and ensure that critical items are always available.
Outsourcing Fulfillment to a Third-party Logistics Provider
3PL providers use state-of-the-art inventory management systems that enable real-time tracking and accurate forecasting, reducing the risks of stockouts or overstocking. 3PL's deep knowledge of best practices in logistics, warehousing, and distribution ensures that inventory is stored and delivered efficiently, optimizing overall operations and allowing companies to focus on their core competencies, such as product development and marketing, while benefiting from the increased efficiency and accuracy provided by the 3PL's advanced systems and expertise.
9. Get Started with SFC Services
SFC stands at the forefront of order fulfillment with cutting-edge facilities in Shenzhen, China. Utilizing sophisticated software, we specialize in seamless and trustworthy fulfillment solutions for ecommerce, dropshipping, and crowdfunding platforms. At SFC, we are dedicated to accelerating your business growth through secure warehousing, efficient processing, customizable packaging options, and adaptable shipping strategies while saving you time and money.
Whether you have or do not have a fulfillment partner, particularly your products manufactured in China, you should consider SFC. Click the button below and get help from SFC logistics experts.
Whether you have or do not have a fulfillment partner, particularly your products manufactured in China, you should consider SFC. Click the button below and get help from SFC logistics experts.
What Makes SFC Special
Over 17 Years of 3PL and Order Fulfillment Experience
All-in-one Tracking Number
Popular Platform API Integration
30 Days of Free Storage
No Hidden Fee
Custom Packaging
Worldwide shipping solutions
Value-added Services
All-in-one Tracking Number
Popular Platform API Integration
30 Days of Free Storage
No Hidden Fee
Custom Packaging
Worldwide shipping solutions
Value-added Services
10. FAQs about Inventory Management
1. What are the main objectives of inventory management?
The main objectives include ensuring product availability, minimizing holding costs, maximizing efficiency, and improving customer satisfaction.
2. How does inventory management affect customer satisfaction?
Effective inventory management ensures that products are available when customers need them, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
3. What are the consequences of poor inventory management?
Poor inventory management can result in stockouts, overstocking, increased holding costs, lost sales, and decreased customer satisfaction.
4. How can small businesses improve their inventory management?
Small businesses can improve by using inventory management software, implementing best practices, conducting regular audits, and training employees.
5. What is the difference between inventory management and inventory control?
Inventory management encompasses the overall process of managing inventory, while inventory control focuses specifically on maintaining accurate inventory records and minimizing discrepancies.
 Post Views:1274
Post Views:1274
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
Next Post
TAGS
Hot Research
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.





 TAGS:
TAGS: